How Are Immune Cells Able to Detect Foreign Pathogens
This enables the immune system to detect just about any pathogen but the detection may take some time during which the pathogen will be replicating and causing harm. TH17 cells are named for their ability to produce interleukin 17 IL-17 a signaling molecule that activates immune and non-immune cells.

11 3d Pathogen Recognition Biology Libretexts
Lymphocytes detect that the proteins and pathogens are foreign - not naturally occurring within the body - and produce antibodies.
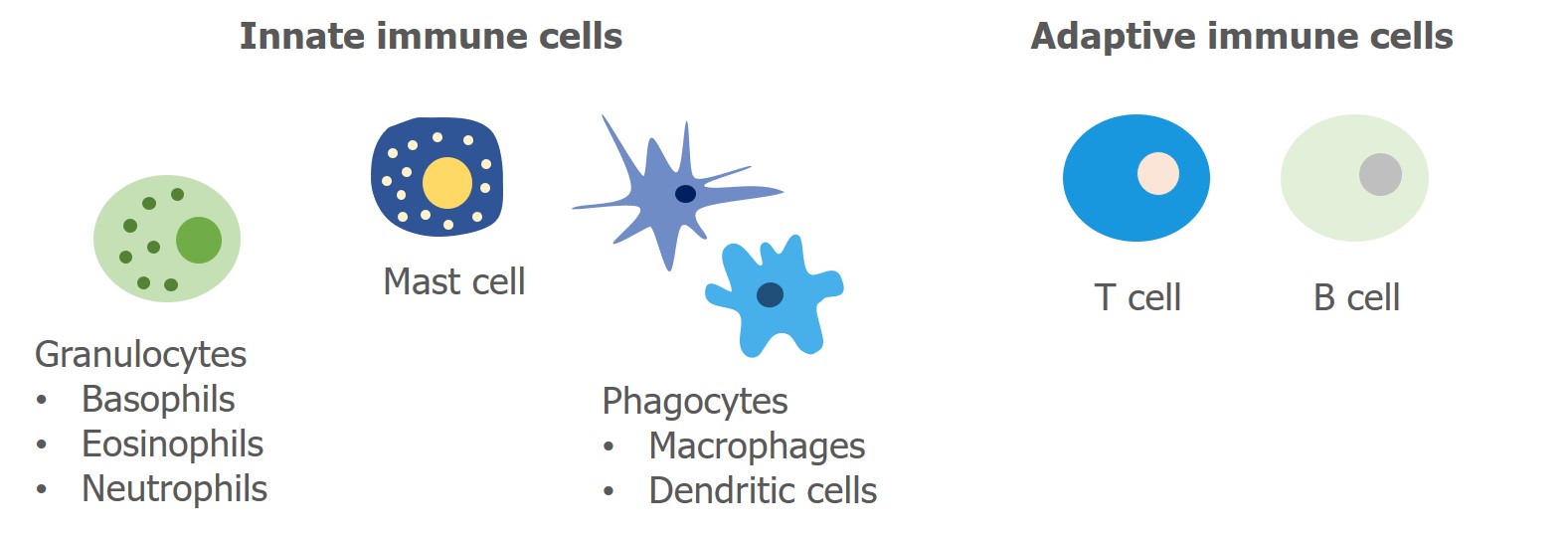
. How Do Immune Cells Detect Infections. The host uses both innate and adaptive mechanisms to detect and eliminate pathogenic microbes. With innate immune cells there is.
Containing the largest collection of phagocytic cells in the body this organ is an important barrier between us and the outside world. Importantly as portal blood also transports a large number of foreign but harmless. The immune system is a vast and complex interconnected network of many different organs cells and proteins that work together to protect the body from illness.
The immune system recognizes. This can take a few days during which time you may feel ill. For T cells to detect and kill foreign pathogens such as clumps of bacteria or viruses the cells must first be triggered into action and transform from inactive and harmless immune cells into.
Antigens are any substances that the immune system can recognize and that can thus stimulate an immune response. Your immune system can recognize cells based on the proteins present on the surface of cells. Researchers are using computer simulations to shed light on how immune cells may identify foreign antigens.
Briefly describe the recognition of non-self by innate immune cells. To protect the body from disease it must recognize and attack these pathogens without damaging its. In other words these cells recruit even more cells to help fight the pathogen.
The immune system needs to be able to tell self from non-self. Nonliving substances such as toxins chemicals drugs and foreign particles such as a splinter can also be antigens. June 7 2013 Source.
The molecules that do the transporting are called MHC molecules. The function of the immune system is to distinguish between the bodys own cells and pathogens. If antigens are perceived as dangerous for example if they can cause disease they can stimulate an immune response in the body.
Healthy cells in the body contain self-antigens which act as important flags to prevent the immune system from attacking the bodys own cells. If a virus has infected a cell MHC can carry viral proteins to the cell surface and present them where the immune system can detect the presence of foreign proteins. The immune system needs to be able to both.
Central to the immune systems ability to mobilize a response to an invading pathogen toxin or allergen is its ability to distinguish self from non-self. Macrophages and neutrophils respond to invasion by foreign pathogens engulf and digest recognized foreign cells. Researchers at McGill University have discovered how immune cells are able to identify foreign antigens.
Ideally positioned to detect pathogens entering the body via the gut the liver appears designed to detect capture and clear bacteria viruses and macromolecules. Second to maintain tissue integrity colonial forms have to rely on their capacity of selfnonself discrimination to rapidly detect approaching allogeneic cells as foreign and to eliminate them. Sometimes one of your own cells changes or mutates giving the cell the ability to multiply continuously.
A surprisingly simple solution linked to the. How are immune cells able to detect foreign pathogens. Rather than foreign pathogens or faulty cells.
First in the absence of specific immune cells cnidarians must have effective mechanisms to defend against microbial pathogens. Pattern recognition receptors PRRs recognise pathogen associated molecular patterns PAMPs which arent present in host cells eg. The pattern recognition theory required the identification of germline-encoded receptors PRRs which can detect pathogens that have entered the cells along with the substances that are naturally identified by the cell for immune activation without the education of a selection process.
During an immune response cells detect invaderforeign cells communicate alarm recruit immune cells suppress or destroy invader. Viruses bacteria and other foreign cells are recognized as being different from your own cells and are attacked by your immune system. Phagocytes recognise pathogens and the toxins they may produce as foreign bodies by the presence of their different non-self antigens.
It does this by detecting proteins that are found on the surface of all cells. In other words these cells recruit even more cells to help fight the pathogen. These cells secrete interleukin 2 I-2 which stimulates cell division of T cells and B cells.
TH2 cells are important for coordinating immune responses against extracellular pathogens like helminths parasitic worms by alerting B cells granulocytes and mast cells. Defend against disease-causing microorganisms. Such mutations often are the cause of.
The immune systems job. To cover the space of all possible nonself patterns adequately requires a huge diversity of lymphocyte receptors with relatively low affinity thresholds. B They can compare the DNA sequences from the foreign cells to host DNA.
Its goal is to keep us healthy. A They detect foreign unfamiliar chemical substances released by the invading cells. They engulf and sequester capturetrap these foreign pathogens which.
Molecules remove cellular debris. Monocyte - macrophage system free and fixed. How do immune cells detect infections.
They are proteins expressed mainly by cells of the innate immune system such as dendritic cells macrophages monocytes neutrophils and epithelial cells to identify two classes of molecules. The immune system protects the body from possibly harmful substances by recognizing and responding to antigens. Antigens are substances usually proteins on the surface of cells viruses fungi or bacteria.
C They are able to detect structures on the surfaces of foreign cells that are not found in the host. Antigens may be contained within or on bacteria viruses other microorganisms parasites or cancer cells. Both of these mechanisms include self-nonself discrimination.
A healthy immune system can defeat invading disease-causing germs or pathogens such as bacteria viruses. Pathogen-associated molecular patterns PAMPs which are associated with microbial pathogens and damage-associated molecular patterns DAMPs which are.
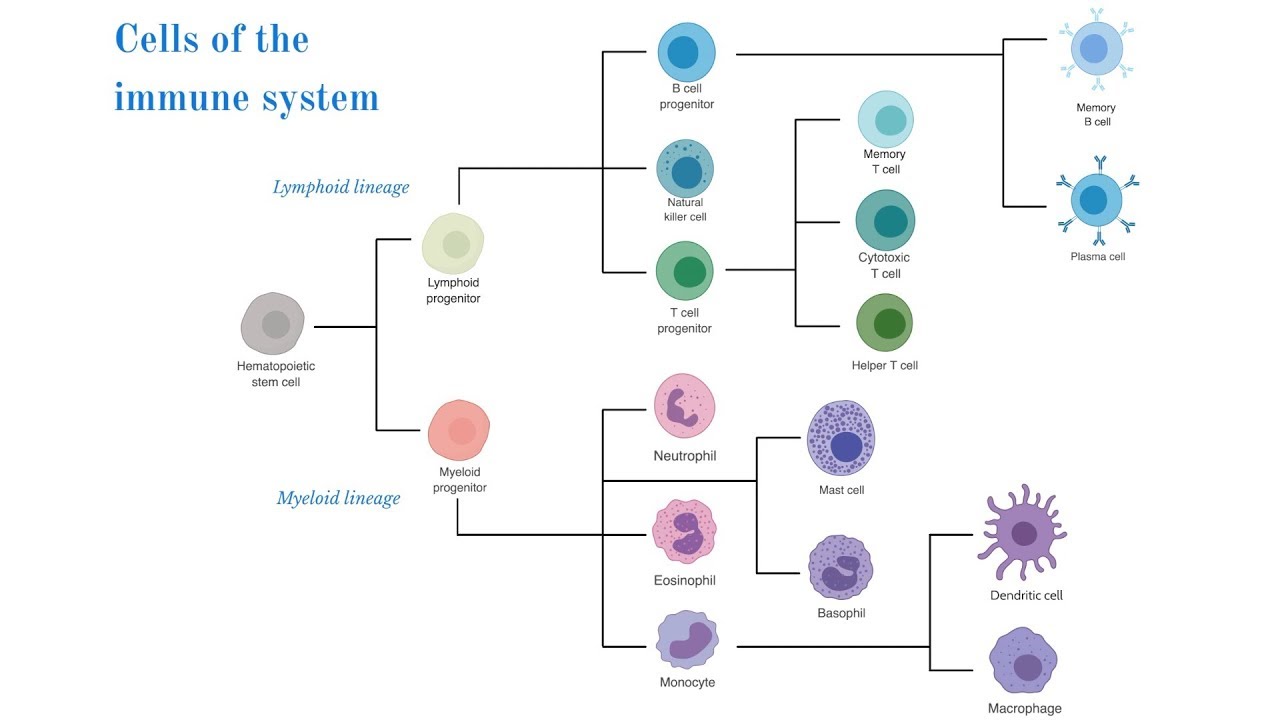
Session 1 Introduction Which Cells Are The Players Ibiology

Comments
Post a Comment